Lakehouse concept:
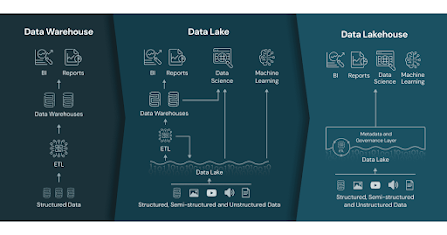
In the context of data management and analytics, a "lakehouse" refers to a modern data architecture that combines the capabilities of data lakes and data warehouses. It aims to address the limitations and challenges associated with these traditional data storage and processing approaches.
A data lakehouse provides a unified and scalable platform for storing, managing, and analyzing large volumes of structured and unstructured data. It incorporates the following key features:
Data Storage: Similar to a data lake, a lakehouse enables the storage of raw and unprocessed data in its native format. This includes structured data (e.g., relational databases, CSV files) and unstructured data (e.g., logs, sensor data, images). By using a common storage layer, such as a distributed file system, data can be ingested from various sources without requiring upfront schema design or transformation.
Ref.: https://www.databricks.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/data-lakehouse-new-1024x538.png
ACID Transactions: Unlike traditional data lakes, a lakehouse provides ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactional guarantees. This means that data can be updated, deleted, and queried reliably, ensuring consistency and data integrity. ACID compliance enables the execution of complex analytics workflows and supports real-time and batch processing.
Schema Enforcement: A lakehouse allows for schema enforcement and schema evolution. It enables the definition of a schema upon data ingestion, ensuring that data adheres to a specific structure or schema. This feature makes it easier to maintain data quality, enforce governance policies, and enable self-service analytics.
Data Processing: A lakehouse incorporates data processing capabilities, typically using distributed processing frameworks like Apache Spark. This enables data transformation, cleansing, aggregation, and other data preparation tasks. The processing capabilities are integrated within the same platform, eliminating the need to move data between different systems.
Querying and Analytics: A lakehouse provides SQL-based querying capabilities, allowing users to perform ad-hoc and complex analytics directly on the stored data. It supports both batch processing and real-time streaming analytics, enabling organizations to derive insights and make data-driven decisions in a timely manner.
By combining the strengths of data lakes and data warehouses, a lakehouse architecture aims to provide a more flexible, scalable, and efficient approach to managing and analyzing data. It enables organizations to store and process data in a cost-effective manner while supporting a wide range of data analytics use cases.
Comments
Post a Comment