Needs for Graph Database:
We are living in the era of data, data is treated more precise than gold and platinum. Most of the enterprises are trying to get more insight about the data they have it as an operational / warehouse / analytical.
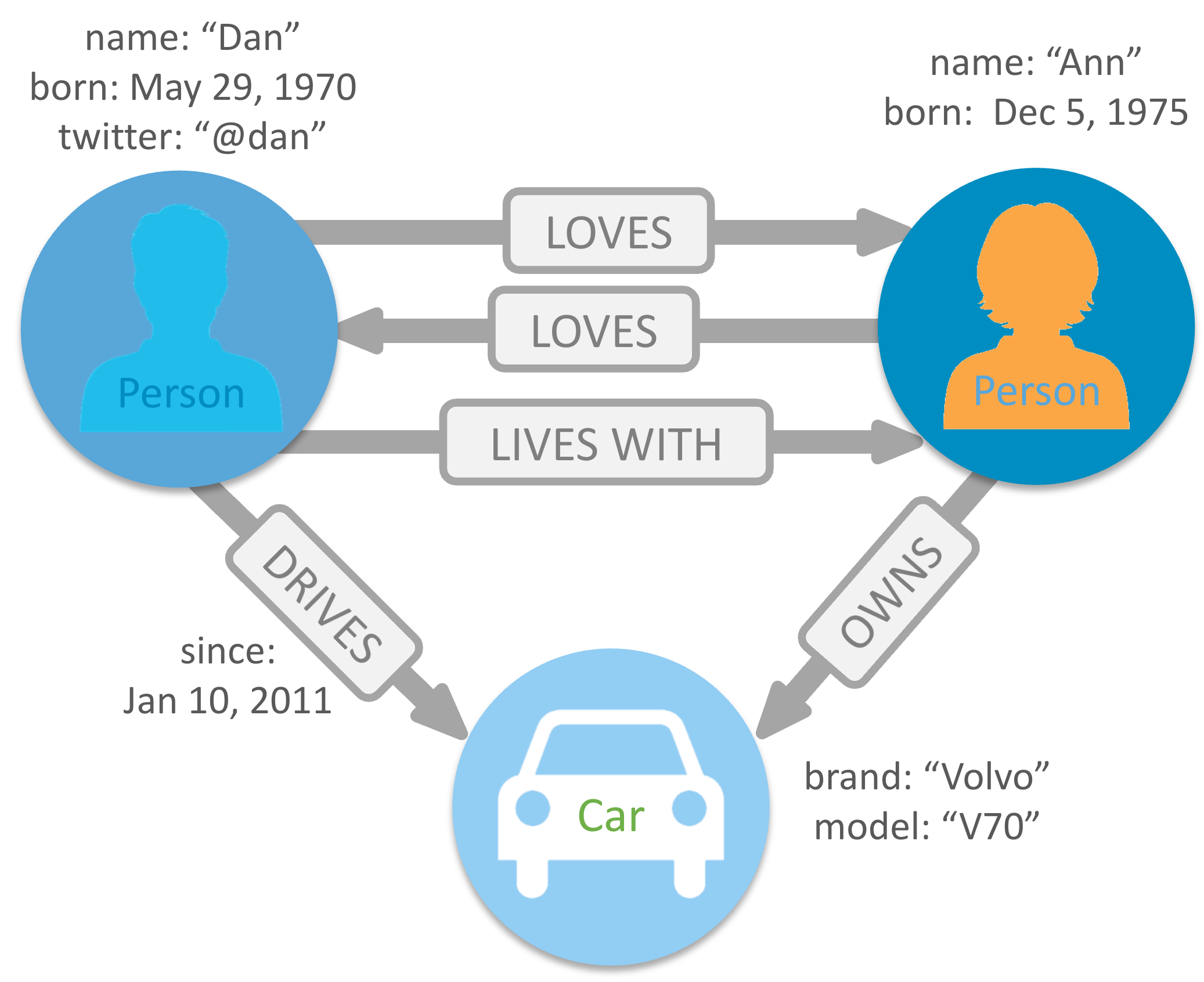
Ref.: https://dist.neo4j.com/wp-content/uploads/graph-example.png
To get more insight into the data, it is required to see the relationship among the data points. The challenge is how to establish the relationship among data points and the answers is Graph database. Relational databases can't help to establish the relationship among data points, due to their rigid schema, and consistent schema.
Relational Database issues for data set:
Number of Joins:
While fetching data from relational databases, we join many tables, these joins are complex, and consume considerable amount of computing resources, which increase the query response times.
Self- joins:
For database ware house / business intelligence systems using RDBMS, self-JOIN are common for hierarchy and tree representation of data such as employee, and manager. When we traverse relationship by joining themselves, it results in an inefficient approach to retrieve the data.
Schema Changes:
Relational databases are not designed for frequent schema changes, and pivots. We are living in the era of agility, which requires frequent schema changes and flexibility.
Slow Queries:
Even though expert DBA put all efforts, use all tricks such as materialized view (computing past results ahead of time) , de normalize the entities to speed up the query, still queries are not fast enough to server the current business needs.
Graph database has the ability to address the issues, challenges of the RDBMS, let us explore
Benefits of Graph database:
Agility:
In current agile software development process / method, test-driven development is an essential part. Modern Graph databases have features to server friction-less development, and graceful system maintenance.
Flexibility:
As we all know the speed does matter in current throat cut competition for the business, IT and data architect has to move at the speed of business. The structure and schema of graph data model is flexible and run with the needs of business. The IT team can add to the features require to the existing graph structure without endangering existing functionality.
Performance:
Graph database can deliver consistence performance even though the data grows every year. Graph database can handle very efficiently the data relationship. Graph database can deliver performance by several magnitude compared to RDBMS.
Ref.: https://neo4j.com/blog/why-graph-data-relationships-matter/
This helped me boost my FPS in Roblox without any lags! Roblox FPS Unlocker really made a noticeable difference in my gameplay. Totally worth trying for smoother performance!
ReplyDelete