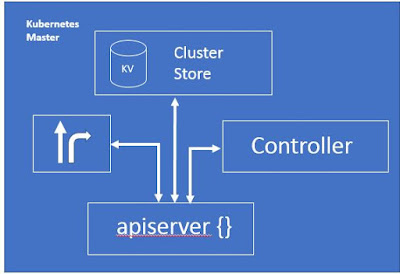
Kubernetes Master (Control Plane):
Kubernetes master is a collection of small specialized services, API server, the cluster store, the controller manager, and the scheduler which makes the control plane of the cluster, for production environment multi-master is must have.EKS-Elastic Kubernetes Service from Amazon, GCP- Google Cloud Platform from Google, Azure from Microsoft are deploying highly available masters.
Most of the time application work load runs on nodes and not on Masters.
The API Server:API server is the brain of the cluster, the front end to into the Kubernetes Masters, Expose RESTFUL API which consume JSON, user POST manifest file to the API server which get validated and then deployed to the cluster. API Server is central management entity and it is the only one entity directly communicate with etcd distributed storage component.
Kubernetes master is a collection of small specialized services, API server, the cluster store, the controller manager, and the scheduler which makes the control plane of the cluster, for production environment multi-master is must have.EKS-Elastic Kubernetes Service from Amazon, GCP- Google Cloud Platform from Google, Azure from Microsoft are deploying highly available masters.
Most of the time application work load runs on nodes and not on Masters.
Ref.: https://www.openshift.com/blog/kubernetes-deep-dive-api-server-part-1
The Cluster Store: Cluster store is the memory of the cluster, which store configuration and cluster state, it is vital to its operation. Without cluster store cluster does not exist. Cluster store is based on etcd, the distributed, consistent and watchable key-value store. Make sure to protect it, so you can recover it, if things go wrong.
Controller Manager: (kube-controller-manager) includes things like the node controller, endpoints controller, namespace controller etc. watch for the changes and make sure current state of the cluster matches the desired state.
Endpoint controller - Populates the Endpoints object (that is, joins Services & Pods).
Service Account & Token controllers: Create default accounts and API access tokens for new namespaces.
Replication controller: Responsible for maintaining the correct number of pods for every replication controller object in the system.
Node controller: Responsible for noticing and responding when nodes go down.
Ref.: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/
Scheduler:(kube-scheduleer) watches for new workloads and assigns them to nodes. Behind the scene it evaluate affinity, anti-affinity, constraints, and resource management.
Kubernetes Nodes:

Nodes used to be called minions for older version of the Kubernetes. Kubelete, container runtime, and kube-proxy are the components of the Nodes.
Kubelet:
Kubelet is the main Kubernetes agent, which run on all cluster nodes. When you install Kubelet on a Linux host, it register host with the cluster as a Node. Kubelete watches the API server for work assignment.
At any instance if Kubelete can't execute particular work task then it reports to master, and master take care what to do with the task. Default port for Kubelet is 10255, which is available for inspection. Kubelet job is to report master (control plane), when it can't execute work.
Container Runtime:
Kubelet works with container runtime to manage container management items such as pulling image, start container, stop containers. Kuberenet uses Docker container, which is default. In future Docker container could be replace by CRI - Container Runtime Interface.
Kube-proxy:
It is a Network brain of the node. Pod gets its own unique IP address by Kube-proxy. It also does light weight load balancing on the node.
Manifest Files:
Manifest files could be either YAML or JSON, posted to API server (Kubernetes Master / Control plane) on port 443, using command line tool kubectl. It instruct Kubernetes how application to looks. It has desired state of the application. It contains which image to use, how many no. of replicas to have, which network to operate on, and how to perform update.
Process Flow:
Manifest file posted on Master by kubectl --> Inspected on on master by Kubernetes -> Identifies the controller (Deployment controller) on master --> Records the config file in cluster store --> Work load issued to Nodes in the cluster --> Node pull the image, start container, build networks. In background Kubernetes sets up reconciliation loops that monitor state of the cluster, if the state varies from the desired state then Kubernetes will use the manifest file to fix it.
Kubernetes Master (Control Plane) and Nodes:
Ref.: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/
The Cluster Store: Cluster store is the memory of the cluster, which store configuration and cluster state, it is vital to its operation. Without cluster store cluster does not exist. Cluster store is based on etcd, the distributed, consistent and watchable key-value store. Make sure to protect it, so you can recover it, if things go wrong.
Controller Manager: (kube-controller-manager) includes things like the node controller, endpoints controller, namespace controller etc. watch for the changes and make sure current state of the cluster matches the desired state.
Endpoint controller - Populates the Endpoints object (that is, joins Services & Pods).
Service Account & Token controllers: Create default accounts and API access tokens for new namespaces.
Replication controller: Responsible for maintaining the correct number of pods for every replication controller object in the system.
Node controller: Responsible for noticing and responding when nodes go down.
Ref.: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/
Scheduler:(kube-scheduleer) watches for new workloads and assigns them to nodes. Behind the scene it evaluate affinity, anti-affinity, constraints, and resource management.
Kubernetes Nodes:

Nodes used to be called minions for older version of the Kubernetes. Kubelete, container runtime, and kube-proxy are the components of the Nodes.
Kubelet:
Kubelet is the main Kubernetes agent, which run on all cluster nodes. When you install Kubelet on a Linux host, it register host with the cluster as a Node. Kubelete watches the API server for work assignment.
At any instance if Kubelete can't execute particular work task then it reports to master, and master take care what to do with the task. Default port for Kubelet is 10255, which is available for inspection. Kubelet job is to report master (control plane), when it can't execute work.
Container Runtime:
Kubelet works with container runtime to manage container management items such as pulling image, start container, stop containers. Kuberenet uses Docker container, which is default. In future Docker container could be replace by CRI - Container Runtime Interface.
Kube-proxy:
It is a Network brain of the node. Pod gets its own unique IP address by Kube-proxy. It also does light weight load balancing on the node.
Manifest Files:
Manifest files could be either YAML or JSON, posted to API server (Kubernetes Master / Control plane) on port 443, using command line tool kubectl. It instruct Kubernetes how application to looks. It has desired state of the application. It contains which image to use, how many no. of replicas to have, which network to operate on, and how to perform update.
Process Flow:
Manifest file posted on Master by kubectl --> Inspected on on master by Kubernetes -> Identifies the controller (Deployment controller) on master --> Records the config file in cluster store --> Work load issued to Nodes in the cluster --> Node pull the image, start container, build networks. In background Kubernetes sets up reconciliation loops that monitor state of the cluster, if the state varies from the desired state then Kubernetes will use the manifest file to fix it.
Kubernetes Master (Control Plane) and Nodes:
Ref.: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/

Comments
Post a Comment